Focus on Cutting-Edge Technologies and Spearhead the Innovation and Development of the Optoelectronic Industry
The 2022 IPEC Annual Report Details the New Progress Made in Cutting-Edge Optoelectronic Technologies That Include 800G and Co-Packaged On-Board Optics
Introduction: The development of 5G, big data, and cloud computing has led to a surge of data on layered branch lines in the information society system, placing increased strain on network bandwidth. Since the slowdown of Moore’s Law that guides the development of microelectronics, optoelectronic integration technologies are increasingly used to provide new technical paths for reducing I/O power consumption and improving bandwidth. As one of the key disruptive innovations in the optoelectronic industry, optoelectronic integration technologies combine photons and integrated circuit electrons, and even replace electrons with photons, thereby expanding the “fiber-in and copper-out” transformation to chips for on-chip optical interconnect and reshaping the existing optical module industry chain. In the 2022 annual report, the International Photonics & Electronics Committee (IPEC) issued the phased progress that has been made in standardization of high-speed optical interconnection and cutting-edge optoelectronic technologies.
At a recent conference of the joint committee work group, IPEC released its 2022 annual report, paying special attention to the rapid development of IPEC during that year. With the joint efforts and active contributions of all members and industry experts, IPEC has made phased progress in the research of key optoelectronics projects, such as 400G/800G high-speed optical connectivity, next-generation wireless optical technologies, and Optical Input/Output (OIO) chips. Furthermore, the phased progress has promoted the standardization process of the entire optoelectronic industry.
At the beginning of its establishment, IPEC attracted leading organizations and enterprises in the optoelectronic field with the purpose of openness, fairness, unity, and innovation. With its technical work group operations and active participation of team members, IPEC continuously promotes standards for both collaboration and innovation in the optoelectronic field. IPEC has released a series of research achievements in international standards and industry forums, which are highly recognized in Optoelectronic circles and attract more and more partners’ attention. The number of IPEC members has jumped from 13 in the initial phase to more than 40, covering the upstream and downstream sectors of the optoelectronic industry chain. In addition, IPEC was invited to introduce its progress at the OIF Q122 plenary meeting and has established a long-term cooperation agreement with the Optical Internetworking Forum (OIF) on projects such as 800GLR IA and OIO.
In this annual report, IPEC released the following research projects and details their progress in these key fields:
New Optical Interconnection Solution Provides a Technical Path for Data Center Switching Networks to Evolve to Beyond 100T
To meet the requirements of data center switching networks for lower power consumption and lower costs, IPEC proposed a new optical interconnection solution, which uses a combination of OIO (co-packaged on-board optics) and Pluggable External Light Source (PELS) technologies to meet the optical I/O requirements of switches using application-specific integrated circuit (ASIC) chips with a capacity beyond 100T. In view of this, the Advanced Technology Work Group of IPEC initiated the 100T+ OIO research project, and the Form Factor Work Group initiated the OIO PELS project (related to interface standards), to study the requirements, challenges, and key technologies of 100T+ data switching networks and devices from multiple aspects, such as the DCN, switching device, optoelectronic packaging component, and optical engine. These projects aim to support future standards and product development. Currently, the research report Draft 1.0 of the OIO project has been baselined, and the OIO PELS project is under specification discussion.
Currently, the application of the OIO technology in switches needs to be achieved through combining optical engines (OEs) and laser sources. An illustrative diagram of OIO application is shown in Figure 1, in which, for example, a 51.2 Tbit/s switch consists of an ASIC chip, 16 OEs, and 16 PELSs. Each OE transmits 3.2 Tbit/s services with a total of 32 LD/Rx channels and provides optical I/O to the switch ASIC through optical connections. The external laser source (ELS) produces a continuous wavelength (CW) laser light for OEs to convert the electrical signal output from ASIC into an optical signal using external modulation solutions. With an OE silicon split ratio of 1:4, and each PELS containing eight lasers, a PELS can provide laser sources to a 3.2 Tbit/s (4 x 8 x 100 Gbit/s) OE. PELSs provide higher reliability, operability, maintainability, and stability than on-chip light source solutions. By applying the OIO technology to switches with shorter electrical links from ASICs to OEs, there is an expected improvement in both the signal quality and bandwidth as well as a reduction in power consumption.
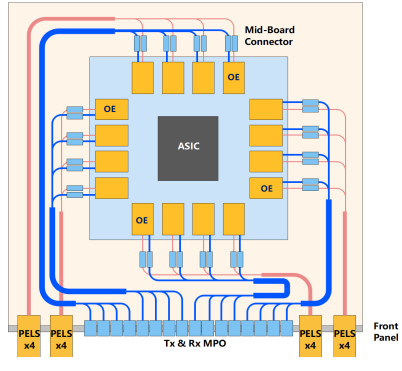
Figure 1 Application of PELS-based OIO in a switch
IPEC uses the PELS solution with a single MT connector. Compared with a solution with dual MT connectors, this solution has the following features:
- Higher dustproof performance
- Higher durability, negating further fool-proof coupling ring design
- Better force balance, all-time symmetric form factor contact
- Higher economic efficiency (due to the use of a single MT connector)
- Higher system integration density and more compact size
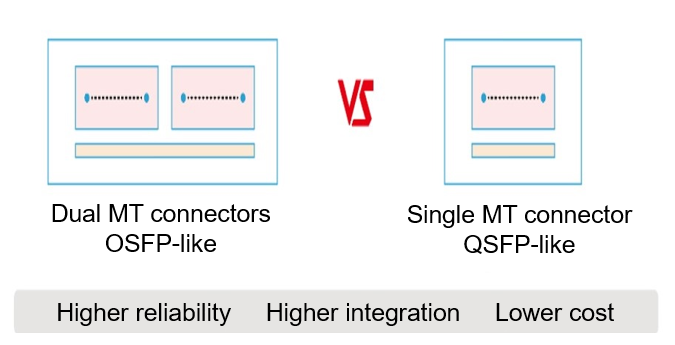
Figure 2 OIO PELS solution with a single MT connector
For the 400G and 800G standards projects oriented to short-haul IDC interconnection, the Physical Media Dependent (PMD) Work Group of IPEC will formulate the 800G standard in two generations. The first-generation 800G standard is based on the 800G optical-layer architecture and optical interface specifications of 100G/lane, and focuses on the 500 m/2 km specifications that are based on single-mode optical fibers to meet the recent market requirements. The first-generation standard has been baselined to version IPEC-IA-800G-D2.0 after discussions about the core scenarios and technologies of 800G optical interfaces with the whole optoelectronic industry chain, including operators, OTT service providers, and vendors of optical modules, components, and packaging. Research on the second-generation 200G/lane-based 800G/1.6T standard is expected to start in 2023. 200G/lane-based solutions can reuse 800G/1.6T applications and integrate with the OIO technology to provide mature and cost-effective next-generation rate standards for the market.
The IPEC officially released the Test Specification for 100 Gbit/s and 400 Gbit/s PAM4 Optical Module at 100 Gbit/s per Lane (test specification for short), which is the industry’s first interoperability test specification for 400G optical modules. It is compiled by the IPEC Plugfest Work Group, along with the China Academy of Information and Communications Technology (CAICT), Accelink, Huawei, Source Photonics, ZTE, and YOFC. This test specification aims to provide the test basis for the evolution of data center networks (DCNs) to 400G, and aid numerous optical module vendors and customers in identifying potential interoperability and compatibility issues and risks in advance, thereby accelerating the large-scale commercial use of 400G optical modules.

Figure 3 Official release of the Test Specification for 100 Gbit/s and 400 Gbit/s PAM4 Optical Module at 100 Gbit/s per Lane
With the gradual commercial use of 400G, the 800G interface standard has become the next research focus of the industry. In December 2022, the Plugfest Work Group of IPEC initiated the 100G/lane-based 800G optical module interoperability test platform project, which aims to provide the industry with an open platform to test the interconnectivity and interoperability of 400G and 800G optical modules. This provides basic data for introducing 400G and 800G technologies to data centers, and lays a solid foundation for applying and promoting high-speed optical modules in data centers through interoperability network testing and performance evaluation.
On February 18, 2022, the webinar themed “Evolution from Pluggable to OIO, Enabling Ultra-Broadband Optical Connectivity for Future Data Centers” was successfully co-hosted by IPEC, China International Optoelectronic Exposition (CIOE), and the European Photonics Industry Consortium (EPIC). During the webinar, experts from different companies and academic institutions, including Arista Networks, Meta (formerly Facebook), Intel, Broadcom, TE Connectivity, UC Santa Barbara, Baidu, Alibaba, and Huawei, had in-depth discussions on high-speed optical connectivity for next-generation data centers, in addition to exploring cutting-edge technologies such as 100+ Tbit/s ultra-large switching capacity in the optoelectronic industry.

Figure 4 OIO webinar hosted by IPEC, CIOE, and EPIC on February 18, 2022
Looking towards the future, joint industry collaboration will rapidly advance optoelectronic technologies such as 800G and OIO like never before. As an open industry standards platform, IPEC has begun research into the innovative 100+ Tbit/s OIO technology. IPEC will focus on addressing the issues and challenges impacting this field, and will gather industry forces to promote the standardization, innovation, and application of next-generation optoelectronic technologies.
Next-Generation Optical Fronthaul Technology Enables the Flexible Improvement of Fronthaul Bandwidth
The operator-oriented next-generation fronthaul optical module evolution project will enable more antennas and frequency bands to be applied in wireless fronthaul scenarios with the evolution of wireless 5G. As the port rate increases from 25 Gbit/s to 50 Gbit/s and even 100 Gbit/s, wireless fronthaul scenarios need to cover a transmission distance up to 10 km and share underlying technologies with data centers as well as transport and access domains. To drive the healthy development and rapid maturity of the mobile fronthaul 50G industry, IPEC approved the Mobile Fronthaul 50G (MFH50) standards project, which was proposed by the Network Requirement Work Group and Form Factor Work Group, at IPEC annual meeting in February 2022. This project aims to coordinate the opinions of operators, equipment vendors, and module vendors to unify the fronthaul industry consensus, study technical challenges and solutions in new scenarios and rates, define key parameters for wireless fronthaul, and provide guidance on the design of chips, and algorithms.
Following an in-depth discussion in the MFH50 project, multiple high-quality proposals have been submitted for existing fronthaul link surveys, optical module line rate specifications, electrical interface parameters and acceptance test solutions, optical parameters of gray optical modules and passive multiplexers/demultiplexers, and O&M requirements of optical modules. The next step of the project will focus on the formulation of the Fronthaul Link White Paper and the research on the optical parameters of colored WDM.
On July 28, 2022, IPEC and LightCounting held a global webinar and invited representatives and technical experts from leading players in the wireless fronthaul field, such as operators, device vendors, optical module vendors, and chip vendors, to discuss next-generation optical fronthaul solutions.

Figure 5 Webinar held by IPEC and LightCounting on next-generation optical fronthaul solutions on July 28, 2022
During the webinar, industry experts reached a consensus on the following aspects:
- There will continue to be multiple different fronthaul network scenarios and solutions, depending on distance, fiber density, and RAN technology. (MOPA lists 19 of them.)
- Some future fronthaul scenarios will require optical transport speeds greater than 25G, ranging from 50G to 800G.
- Chromatic dispersion is one of the main challenges for bringing inexpensive higher speed devices from the hyperscale data center environment to the harsh outdoor RAN fronthaul environment, especially for longer fronthaul distances involved in C-RAN (up to 15 km).
- PAM4 modulation is an attractive solution for 50G optics, with DSPs optimized for wireless applications becoming available.
- SFP56 is the preferred form factor for 50G devices.
- Both colorless and colored (WDM) versions of 50G transceivers are needed for the various passive, semi-active, and active fronthaul architectures.
- 100G BiDi is viewed as a key need for xHaul transport (backhaul access and aggregation) now.
In the future, the IPEC MFH50 project will continue to focus on solving problems and challenges in fronthaul scenarios, and work together with upstream and downstream industry forces to promote the standardization for innovation and industry application of 50G optoelectronic technologies in the fronthaul field.
Gather Industry Forces and Spearhead the Research of Optoelectronic Technology to Promote the Initiation of Optoelectronic Standards Projects Step by Step
With the deepening of industry digitalization and new infrastructure construction, standardization has become an inevitable trend for optoelectronic technologies, one of the most representative leading industries in the world. The founding mission of IPEC is to aggregate industry forces and jointly support the long-term development of the optoelectronic industry through standardization, strategic roadmap research, and industry and technology summits based on fully transparent, fair, and just optoelectronic standards and platforms.
Dr. Li Junjie, IPEC Chairman, said, “After two years of development, IPEC has made some achievements in the field of optoelectronic technologies, with active contributions and support from all members and experts, and has made outstanding achievements in a series of research on cutting-edge optoelectronic technologies, such as OIO, 400G/800G port standards, interoperability test platforms, and next-generation wireless optical solutions. To meet the requirements of increasing application scenarios in the cloud era, optoelectronics technologies are embracing a new round of opportunities and challenges. IPEC will continue to work with industry peers to explore the development direction of cutting-edge optoelectronic technologies in the new business environment.”
At present, many innovative optoelectronic technologies are leading the development and transformation of the industry, and are also influencing and creating application markets. At this moment of robust vitality in the optoelectronic field, IPEC and LightCounting will cooperate again to hold a global webinar on March 22, 2023. The webinar will focus on the application of Linear Transceiver in the data center OIO (OBO/NPO or CPO) optical field.
You can scan the following QR code to register for the conference.

About IPEC
IPEC (www.ipec-std.org) is an international standards organization that is committed to developing open optoelectronic standards and delivering strategic roadmap reports. IPEC focuses on standardizing solutions in optical chips, optical/electrical components, and optical modules. Markets addressed by IPEC include 5G, IoT and AI.
By August 2022, the number of IPEC members has increased from 13 to 41. Currently, the IPEC members include China Telecom, CAICT, Meituan, Huawei, FiberHome, Broadex, CIG, Wenzhou Yihua Connector, Fujitsu Optical Components (FOC), Hisense Broadband, HGGenuine, Source Photonics, Yamaichi, AOI, InnoLight, ZTE, AROPTICS-TECH, Mindsemi, Accelink, O-Net, H3C, YOFC, Foxconn, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Sitrus Technology, Semtech, Advanced Fiber Resources, ATOP Corporation, SiFotonics, Intel, Acon Optics, JONHON, Suzhou GL Foresight Electronic Technology, Liobate, SENKO, Marvell, VIAVI, Yuanjie Semiconductor Technology, Dongguan Luxshare Technology, National Optoelectronics Innovation Center (NOEIC), and Amphenol.
IPEC is open to any interested party who wishes to join. All members have the opportunity to participate in developing all IPEC standards and reports on a non-discriminatory basis. The process of developing these standards and reports is transparent to all members. IPEC is registered in Switzerland.







