IPEC’s OIO Research Project: Exploring the Evolution of Next-Generation Data Center Switching Chips
The innovative application of technology, particularly in regard to the Internet, has greatly accelerated global connectivity and development. Such innovation drives the digital transformation of the social economy, and has led to profound changes in how we interact and do business. Over the past decade, network traffic and connection requirements have increased exponentially, with most traffic closely related to data centers. Optical interfaces providing 100 Gbit/s have been widely deployed for both intra- and inter-DC interconnection, and some enterprises are even promoting the application and deployment of 400G technologies. In addition, interfaces with 800 Gbit/s and over 1 Tbit/s rates are continuously evolving to meet the high bandwidth requirements of data centers and further reduce the cost per bit.
However, the explosive growth of data center traffic introduces numerous challenges in terms of footprint and power consumption. Typically, a large number of servers and communications cabinets are installed in a data center, with highly secure and reliable power supply and cooling devices equipped. As energy conservation and emission reduction goals are taking priority around the world, finding ways to create greener data centers has become a key industry challenge. This trend puts the focus on technological innovation for data center communications and interconnection to further reduce power consumption through technology iteration and cut construction and maintenance costs by improving integration.
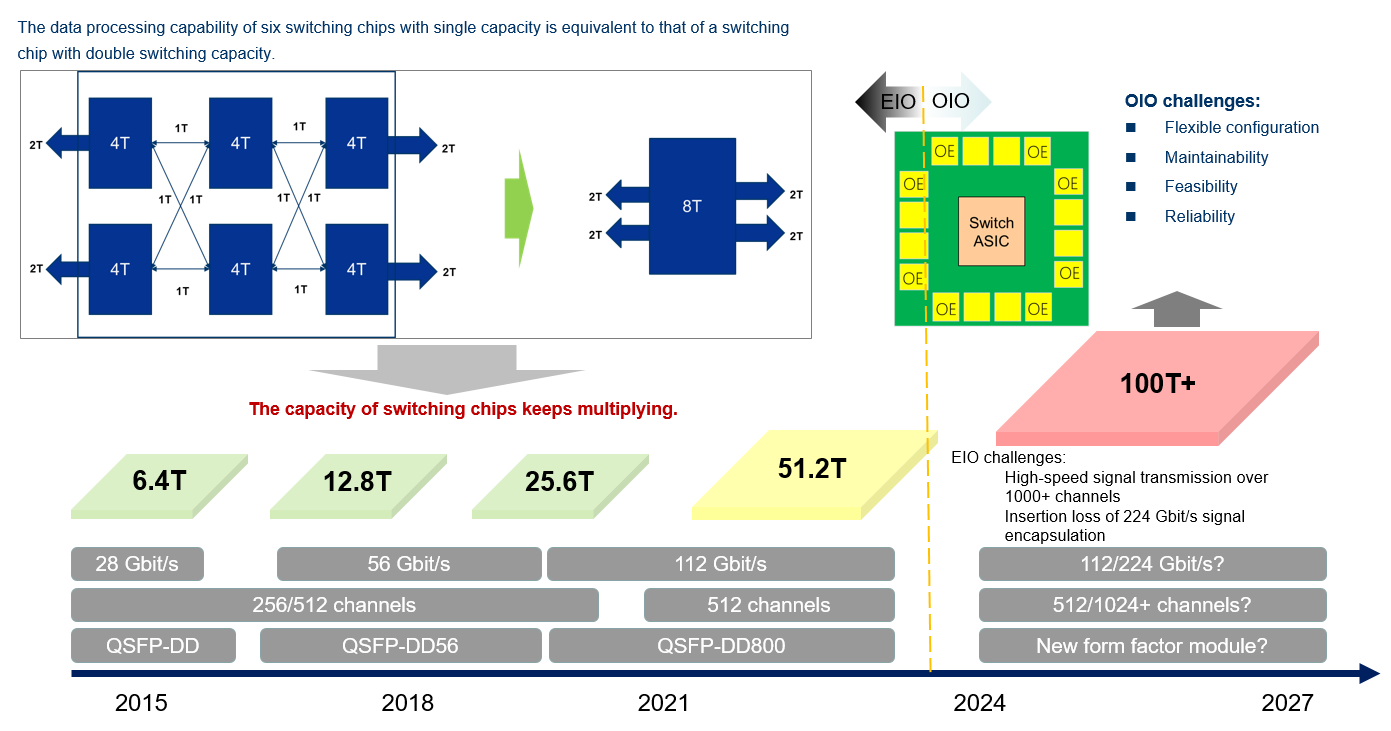
With the development of data center switching networks, the chip capacity of switches has soared to 51.2T. However, due to limitations in the attenuation of high-speed signals and the chip package size, higher requirements are imposed on signal integrity. As a result, chip capacity growth has encountered a bottleneck, and improving the rate of Electrical Input & Output (EIO) interfaces or increasing the number of channels through the use of a pluggable solution is a challenging task.
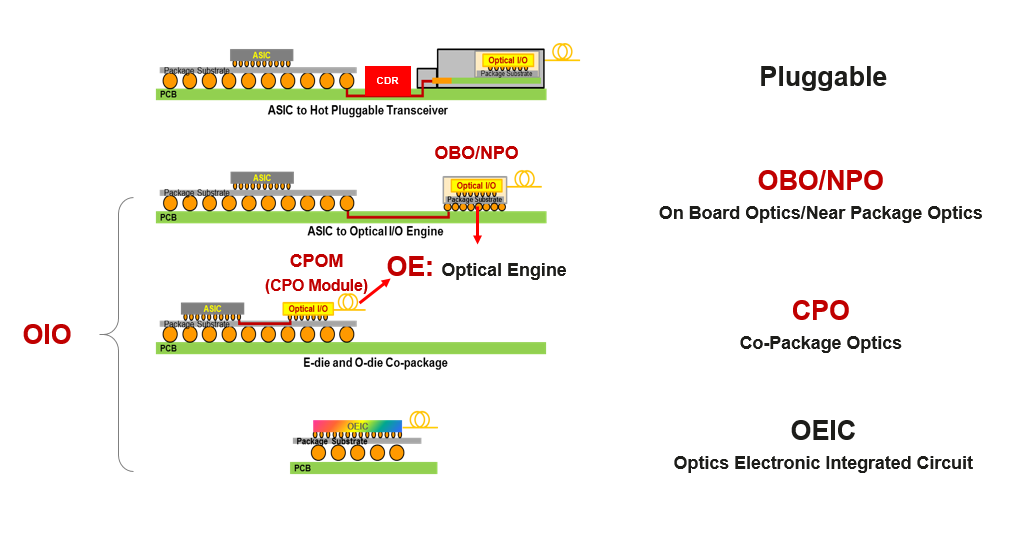
The latest development in the optoelectronic industry — a series of emerging Optical Input & Output (OIO) technologies — may offer a way to overcome these problems. These technologies use high-bandwidth and high-density optical interfaces to address the I/O interface interconnection challenge of large-capacity chips such as switching chips, CPUs, and GPUs. Specific product forms include On Board Optics (OBO), Near Package Optics (NPO), Co-Package Optics (CPO), as well as Optics Electronic Integrated Circuit (OEIC) — a future technology worth keeping an eye on. Compared with the mature EIO technology, OIO is expected to provide 100 times higher channel density, with each channel offering over 100 times the bandwidth. Consequently, OIO is likely to become a necessary technology for switching chips to evolve to 100T, 200T, or even higher capacity.
Within this context, IPEC has launched the 100T+ OIO research project under the guidance of the Advanced Research Work Group. The International Photonics & Electronics Committee (IPEC) was established at the China International Optoelectronic Expo in Shenzhen in September 2020. It has 13 founding members including the China Academy of Information and Communications Technology (CAICT), China Telecom, Meituan, Huawei, FiberHome, Source Photonics, Hisense Broadband, Broadex, CIG, Wenzhou Yihua Connector, Fujitsu Optical Components (FOC), HG Genuine, and Yamaichi, with the number of formal members currently standing at 24. IPEC aims to establish a centralized, open, and transparent standards organization in the optoelectronic field to better support the healthy development of the industry.
To overcome the challenges impacting the Data Center Interconnect (DCI) field, IPEC has researched a series of cutting-edge optical interconnection technologies such as OBO, NPO, CPO, and OEIC. IPEC believes that these technologies have the potential to become application modes for OIO deployment. However, 100T+ switching networks and systems, devices, and optoelectronic components must undergo significant changes if OIO is applied, leading to great challenges in achieving flexible configuration, system maintainability, feasibility, and reliability. Consequently, the Advanced Research Work Group of IPEC initiated the OIO research project to study the network and device requirements, challenges, and key technologies of 100T+ OIO from multiple aspects, such as the Data-centric Network (DCN), switching device, optoelectronic packaging component, and optical engine. This research will identify technical directions, enhance collaborative innovation within the industry chain, and support future standards and product development.
Li Junjie, Chairman of IPEC, said, “Compared with EIO, OIO features higher density and single-channel bandwidth, which will help overcome the I/O design bottleneck of switching chips. However, as a cutting-edge technology, OIO still faces many challenges, which necessitates open discussion and collaborative efforts from the entire optoelectronic industry.”
As an open standard industry platform, IPEC has begun research on innovative 100T+ OIO technologies. In the future, IPEC will focus on addressing the issues and challenges impacting this field, and will gather industry forces to promote the innovation and application of next-generation optoelectronic technologies.
About IPEC
IPEC (http://www.ipec-std.org/) is an international standards organization registered in Geneva, Switzerland that is committed to establishing open, transparent, fair, and impartial optoelectronic standards. It also seeks to build an optoelectronic industry platform that standardizes optoelectronic interfaces and meets the market needs of 5G, IoT, and AI. IPEC focuses on standardizing solutions in optical chips, optical/electrical components, and optical modules to build a unified, open, and compatible standard platform.
By October 2021, the number of IPEC members has increased from 13 to 24. Currently, the IPEC members include China Telecom, China Academy of Information and Communications Technology (CAICT), Meituan, Huawei, FiberHome, Broadex, CIG Shanghai Co., Ltd., Wenzhou Yihua Connector, Fujitsu Optical Components (FOC), Hisense Broadband, HG Genuine, Source Photonics, Yamaichi, AOI, InnoLight, ZTE, AROPTICS-TECH, Mindsemi, Accelink, O-Net, H3C, YOFC, Foxconn, and Shanghai Jiao Tong University.
As an open standards organization, IPEC is seeking new partnerships with operators, cloud service companies, equipment vendors, module vendors, chip vendors, research institutes, and industry partners, to define standards and discuss the development trend of optoelectronic technologies.



