IPEC Initiates the Optical-Layer Standards Research Project for 800G Short-Haul High-Speed Interconnection
With the emergence of services such as 5G, cloud computing, and big data, the volume of Internet services and data computing is skyrocketing. Against this backdrop, data centers (DCs) evolve from siloed to large-scale interconnected structures. This triggers the emergence of data center interconnect (DCI), a technology that connects two or more data centers over high-speed network links. Data centers can be interconnected in one of two ways: intra-DC interconnection for local information storage, generation, and mining, and inter-DC interconnection for data replication, synchronization, and exchange.
According to Cisco’s forecast in the Visual Networking Index (VNI) and Global Cloud Index (GCI), in 2021, only 0.96% of global traffic, equivalent to 0.2 ZB, is not DC traffic. From 2016 to 2021, the compound growth rate of global DC traffic was 25%. This explosion in traffic is driving up DCI networks’ requirements for high-speed optical interfaces. Currently, mainstream Internet enterprises have deployed 100G optical interfaces on a large scale, with construction of 400G networks underway. Considering the soaring bandwidth demands and industry development pattern, there is an urgent need to discuss 800G industry standards.
To promote the development of the 800G industry and its standards system, the International Photonics & Electronics Committee (IPEC) established the Physical Media Dependent (PMD) work group at the beginning of 2021. The work group initiates projects and conducts discussions on multiple key scenarios such as 800G transmission over 500 m, 2 km, 10 km, and 80 km. The members who contributed to the discussions include operators and OTT service providers, as well as optical module, component, and package vendors. The discussions spur resource investment of the whole optoelectronic industry chain on the key scenarios of 800G optical interfaces and encourage relevant technical discussions.
According to a report by the IEEE 802.3 Beyond 400 Gb/s Ethernet Study Group, fiber links account for up to 79% and 95% of network deployments spanning 500 m and 2 km, respectively. Given this, the DR and FR standardization is crucial. After several rounds of discussion, the IPEC’s PMD work group decided to pioneer the development of optical-layer standards for 800G DR8 and 2 x 400G FR4, and to plan to release 800G DR and FR optical-layer standards in the second half of 2022.
|
Inter-DC Transmission Distance
|
Accumulated Proportion of Inter-DC Fiber Links |
| 0–500 m |
79% |
| 0–1 km |
81% |
| 0–2 km |
95% |
| 0–3 km |
99% |
800G DR interface
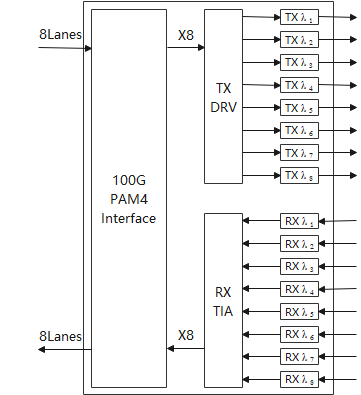
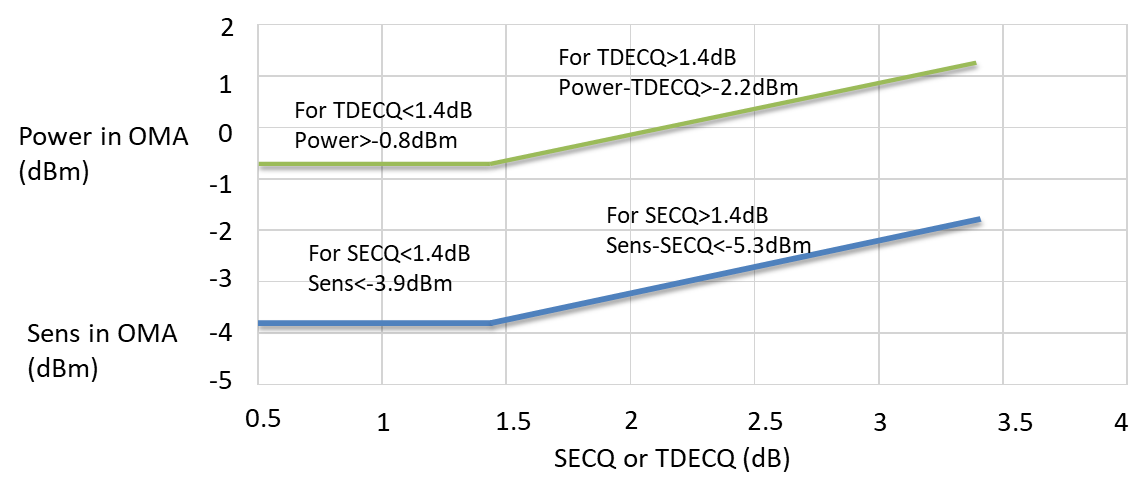
Considering the current state of the industry chain, DR8 is the best solution for 800G transmission over 500 m. DR8 uses the 53 GBaud PAM4 modulation format and 1310 nm wavelength. It properly reuses the resources of the current 400G DR4 optoelectronic industry chain, and drives down the chip design cost to almost zero, meeting the low-cost requirements in DC scenarios. In the future, after 200G per channel is put into commercial use, 800G DR8 will smoothly evolve to 1.6T DR8, ensuring the PSM architecture remains future-proof. The following figure shows the budget of 800G DR8 optical links for 500 m transmission.
800G FR interface
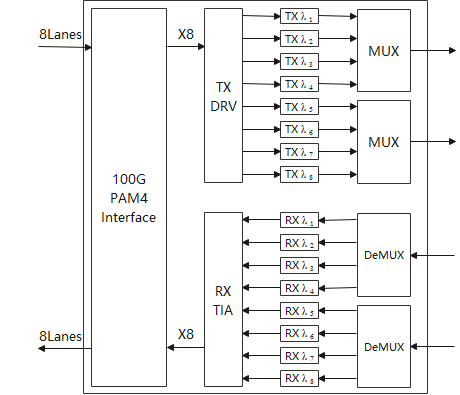
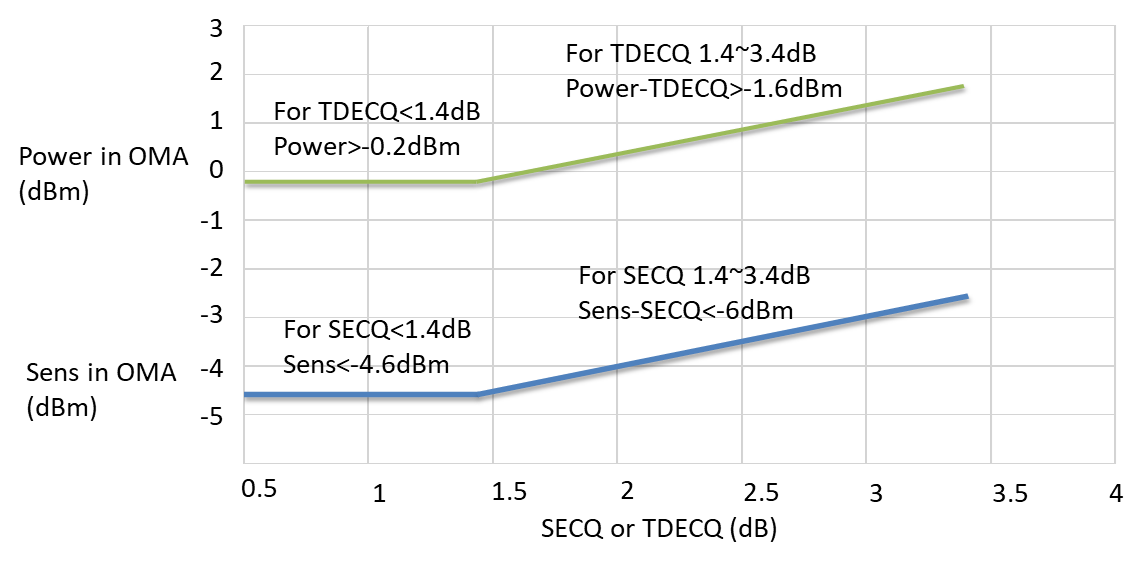
2 x 400G FR4 uses the 53 GBaud PAM4 modulation format and 1271 nm, 1291 nm, 1311 nm, 1331 nm wavelengths. In addition, it reuses the 400G FR4 optoelectronic chip design, achieving fast commercial use with low design costs. In the future, the solution will smoothly upgrade to a 1.6T (2 x 800G) solution. The following figure shows the budget of 2 x 400G FR4 optical links.
For details about the baseline specifications of 800G DR8 and 2 x 400G FR4 optical interfaces, visit http://www.ipec-std.org/data-download.
The 800G transmission discussions of IPEC’s PMD work group is divided into two phases. Before 2023, the focus will be on the first-generation 100G per channel scenario. In the future, the solution will evolve to 200G per channel, covering 500 m, 2 km, 10 km, and 80 km transmission scenarios. IPEC welcomes more industry experts to join in to promote the sustainable and healthy development of the optoelectronic industry.
About IPEC
The International Photonics & Electronics Committee (IPEC) is an international standards organization that is committed to developing open optoelectronic standards and delivering strategic roadmap reports. IPEC focuses on standardizing solutions in optical chips, optical/electrical components, and optical modules. Markets addressed by IPEC include 5G, IoT and AI.
By the end of 2021, the number of IPEC members has increased from 13 to 30. Currently, the IPEC members include China Telecom, China Academy of Information and Communications Technology (CAICT), Meituan, Huawei, FiberHome, Broadex, CIG Shanghai Co., Ltd., Wenzhou Yihua Connector, Fujitsu Optical Components (FOC), Hisense Broadband, HG Genuine, Source Photonics, Yamaichi, AOI, InnoLight, ZTE, AROPTICS-TECH, Mindsemi, Accelink, O-Net, H3C, YOFC, Foxconn, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Sitrus Technology, Semtech, Advanced Fiber Resources, ATOP Corporation, SiFotonics, and Intel.
IPEC is open to any interested party who wishes to join. All members have the opportunity to participate in developing all IPEC standards and reports on a non-discriminatory basis. The process of developing these standards and reports is transparent to all members. IPEC is registered in Switzerland.







